The most prominent aspects of editors are summaries of recent documents of AGU magazine editors.
Fountain: Geophysical Research Letters
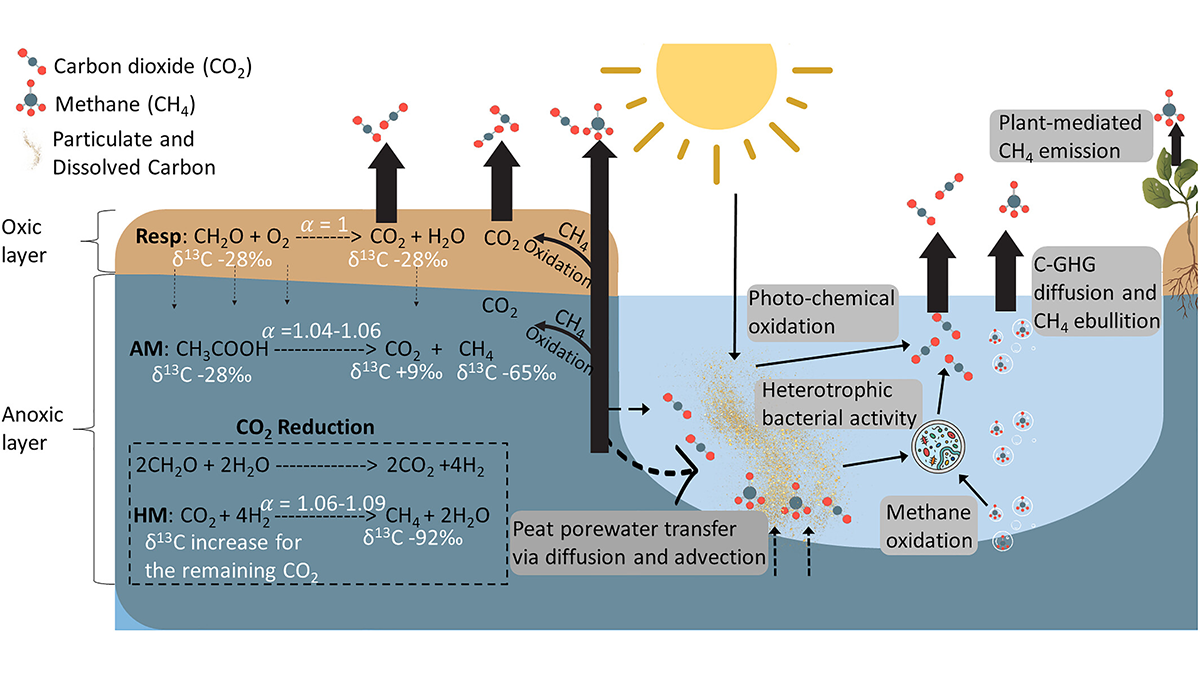
Approximately 41% of Southeast Asia’s turbase forests were affected by the change in land use, and conversion to tree plantations is one of the most common practices. However, data on the production and altered emissions of greenhouse gases in these systems remain extremely limited.
Taillardat et al. [2025] Measure the concentration, composition and age of carbon in water and soil in an industrial acacation plantation of short rotation in Sumatra Tosters, Indonesia. Exceptionally high levels of dissolved organic carbon, carbon dioxide and methane in water and drainage networks were found, indicating that these plantations are hot carbon points. This was a centenary carbon in the water, highlighting the combination of high productivity and exposure of the old dense substrates in carbon to the exposure in a planting environment.
Citation: Taillardat, P., Moore, J., Sasmito, S., Evans, CD, Alfina, T., Lok, S., et al. (2025). Methane production and carbon dioxide and emission routes in the underground water bodies and drainners of a tropical peat planting forest. Geophysical Research Letters52, E2024GL112903. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024gl112903
—Valeriy Ivanov, editor, Geophysical Research Letters
Text © 2024. The authors. CC BY-NC -nd 3.0
Except when indicating otherwise, the images are subject to copyright. Any reuse without express permission of the copyright owner is prohibited.
Related
#Tobble #plantations #Southeast #Asia #hot #carbon #points