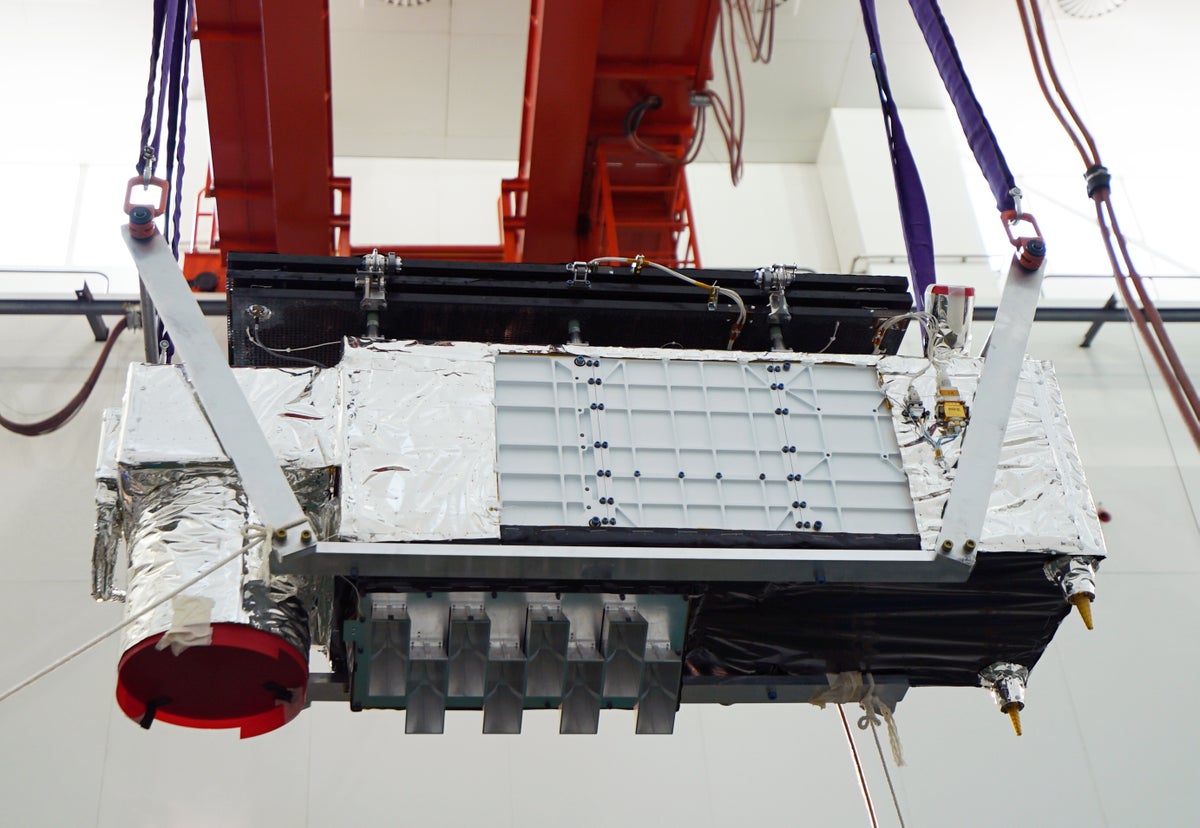
The mini-satellite sends a quantum message encrypted a record distance
Scientists in China have transmitted encrypted images a record of 12,900 kilometers, paving the way for quantum messages anywhere on earth
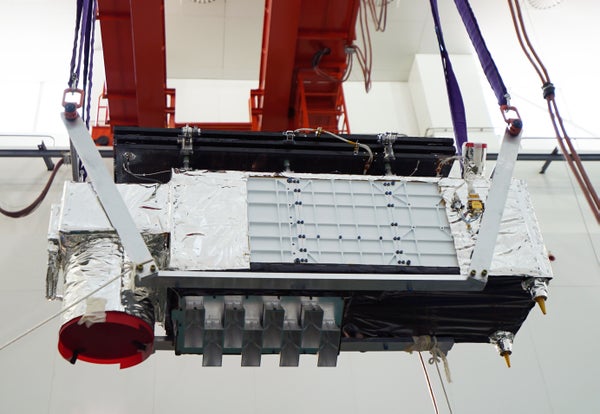
The satellite of the size of a Jinan-1 refrigerator, in the photo before its launch in 2022.
The researchers have broken a record of distance in quantum communication by sending a secret encryption key of almost 13,000 km from China to South Africa, using a cheap and light ‘microsatellite’.
The satellite was able to send laser light pulses, placed in special quantum states, from a roof in Beijing to another at the University of Stellenbosch, near Cape Town. The pulses formed A quantum key that was used to encrypt two images – One of the great wall of China and one that shows part of the Stellenbosch campus. The feat, a kind of encryption known as quantum key distribution (QKD), is a step to send ultra second messages between two locations, however, distant. Was described in nature March 19.
The satellite, called Jinan-1, is ten times lighter, 45 times cheaper and much more efficient than its predecessor, Micius, which was launched in 2016Jian-Wei Pan says, quantum physicist from the University of Science and Technology of Hefei, China, who directed the work.
About support for scientific journalism
If you are enjoying this article, consider support our journalism awarded with subscription. When buying a subscription, it is helping to guarantee the future of shocking stories about the discoveries and ideas that shape our world today.
The PAN team also shrunk the receptor of the fundamental station of 13,000 kg to 100 kg portable. “We want to improve proof technology to really practical and useful,” he says. PAN adds that your team is working with the telecommunications firm based in Beijing China Telecom to launch four more microsatellites for commercial applications in 2026.
“This is another milestone in the development of a global QKD network,” says Alexander Ling, quantum physicist of the National University of Singapore. The satellite is “a significant step” in the deployment of this type of encryption in real time, adds Katanya Kuntz, quantum and co -founder physics of Qubo Consulting, a company based in Calgary, Canada, helps other companies to adopt quantum technologies.

The researchers encrypt these two images using a quantum key, which transmitted from China to South Africa.
China University of Science and Technology
Unwavering codes
Physicists think that future quantum computers You can break many types of encryptionBut techniques such as QKD provide “a very solid guarantee that a future quantum computer cannot read confidential communications,” says Ling.
QKD is already used by banks and governments to transmit keys through fiber optics. But these cables absorb photons, limiting the distance on which the signal can travel. Because the light is absorbed at a much lower speed when traveling through the air than in a fiber optic cable, satellites could act as a relay to send secret keys between two locations almost anywhere on the planet.
Quantum encryption is based on the idea that if two parties share a secret key, they can stir a message so that only they can decode it.
The bread experiment involved sending laser light pulses that are in a ‘overlap’, where there are both in two quantum states, which represent 1 or 0. When comparing the configuration that the sender uses with those used by the receiver to measure the pulses, the two parts can solve a selection of 1 or 0s measured to use as a safe key. If a spy tries to intercept the message, this disturbs quantum states and creates noise, revealing that the key has been compromised.
Faster communication
The configuration involving Jinan-1 includes “several impressive technological achievements,” says Kuntz, a member of the scientific team of quantum encryption and the scientific satellite, a QKD satellite that must be launched next year by the Canadian space agency. Communication between the soil and the satellite is faster than with the previous systems, which accelerates the encryption, she says. The team could also reduce the satellite by giving some of its components two jobs, says bread, for example, using only one piece of kit to aim the beam and control satellite orientation.
However, Jinan-1 cannot do everything that his thickest predecessor could. Does not produce ‘entangled’ photons, which would enable types of encryption that hide the key even of the satellite. In the current system, Jinan-1 processes the key, “and a Spaniard could learn the secret key if [they] The satellite pirate, ”says Kuntz. Entanglement will also need to Connect quantum computers worldwide as part of a quantum Internet. The miniaturization of technology for tangle is more difficult, but the development of microsatellites with this team will be “completely feasible” in the future, says PAN.
They are currently preparing around a dozen quantum satellites to launch throughout the world, says Ling, Speqtral co-founder, a Singapore-based firm that works on QKD satellites even smaller and smaller and light that Jinan-1. “This area is beginning to see an increase in investment and activity as companies and organizations begin to explore the possibility of a global QKD network,” he says.
This article reproduces with permission and it was First published March 19, 2025.
#minisatellite #sends #quantum #message #encrypted #record #distance