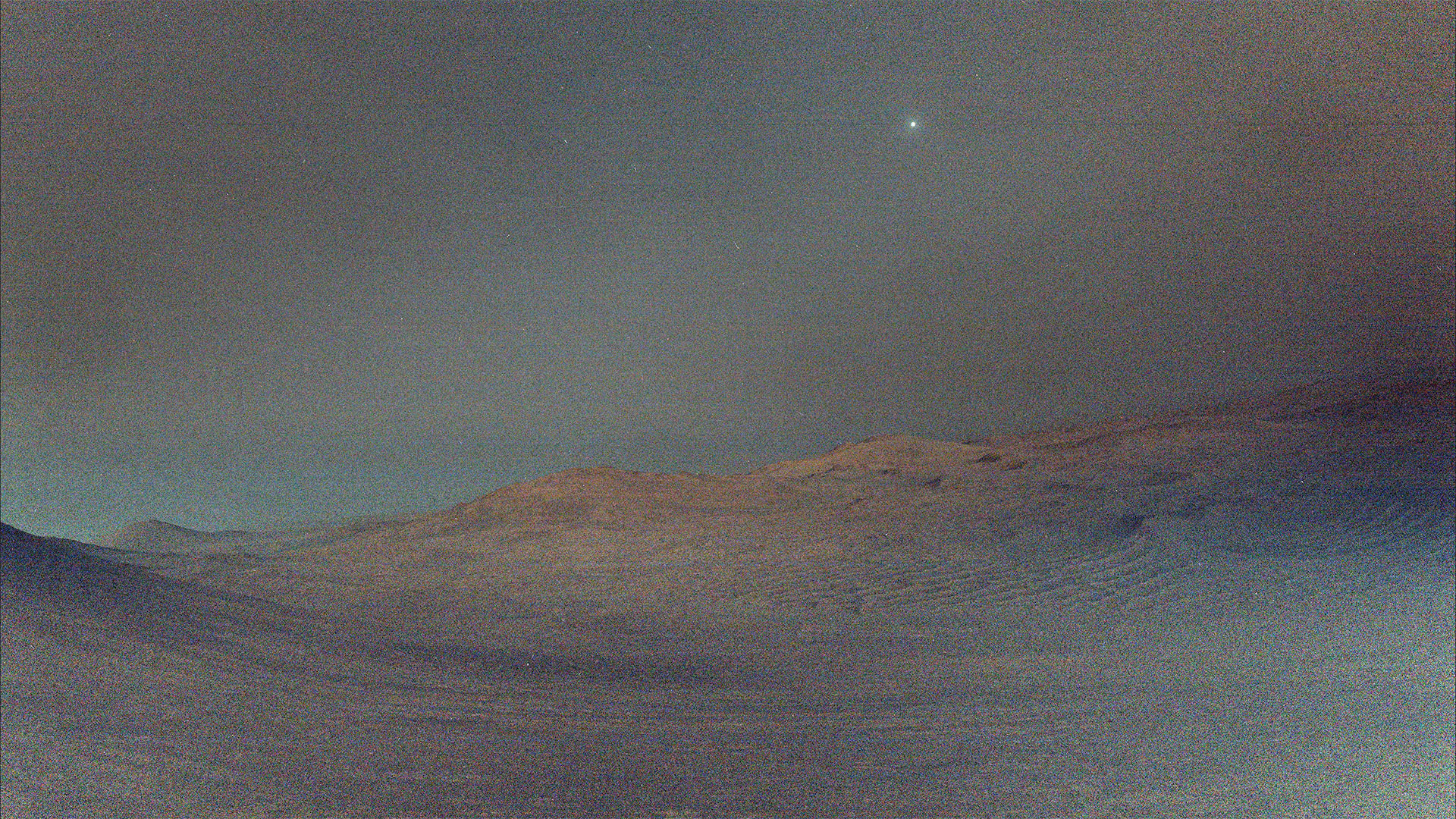
NASA’s perseverance rover captured this view prior to the dawn of the Mars de Mars hanging on a Martian view with little light.
What is it?
Unlike the Earth’s moon, which is approximately a quarter of the planet size, Deimos is less than 1/500 the size of Mars. That means that when seen in the night sky, as seen here at 4:27 am local time on March 1, 2025, the 1,433º Martian day, or sun, of the perseverance mission, seems more like a star than a heavenly body.
Deimos measures only 7.8 miles (12.6 kilometers) wide.
Where is?
We complete an orbit around Mars every 30 hours and 17 minutes at an average distance of 14,576 miles (23,458 kilometers) of the Martian surface.
At the time this photo was taken, the perseverance rover was reaching a place called “Witch Hazel Hill”.
Another feature, “Woodstock Crater”, in the center to the right, is approximately half mile (750 meters) of the rover.
Why is it incredible?
This view is the product of 16 individual shots, that perseverance assembled in a single photo that later transmitted to Earth.
In the dark before dawn, the left navigation chamber of the rover needed to use its maximum exposure to long exposure of 3.28 seconds for each of the 16 snapshots. In total, the image represents an exposure time of approximately 52 seconds.
The image is nebula because the exhibitions of little light and long can add digital noise to the images of perseverance. Many of the white motorcycles in the sky are probably noise, with others the effects of cosmic rays. Two of the brightest white motorcycles are Regulus and Algieba, stars that are part of Leo’s constellation.
Do you want to know more?
You can read more about Deimos and the perseverance of NASA Mars Rover.
You can also read about another view in the Martian sky, since perseverance has become the first spacecraft to detect auroras from the surface of another world.
#Perseverance #observes #photo #moon #Mars #day