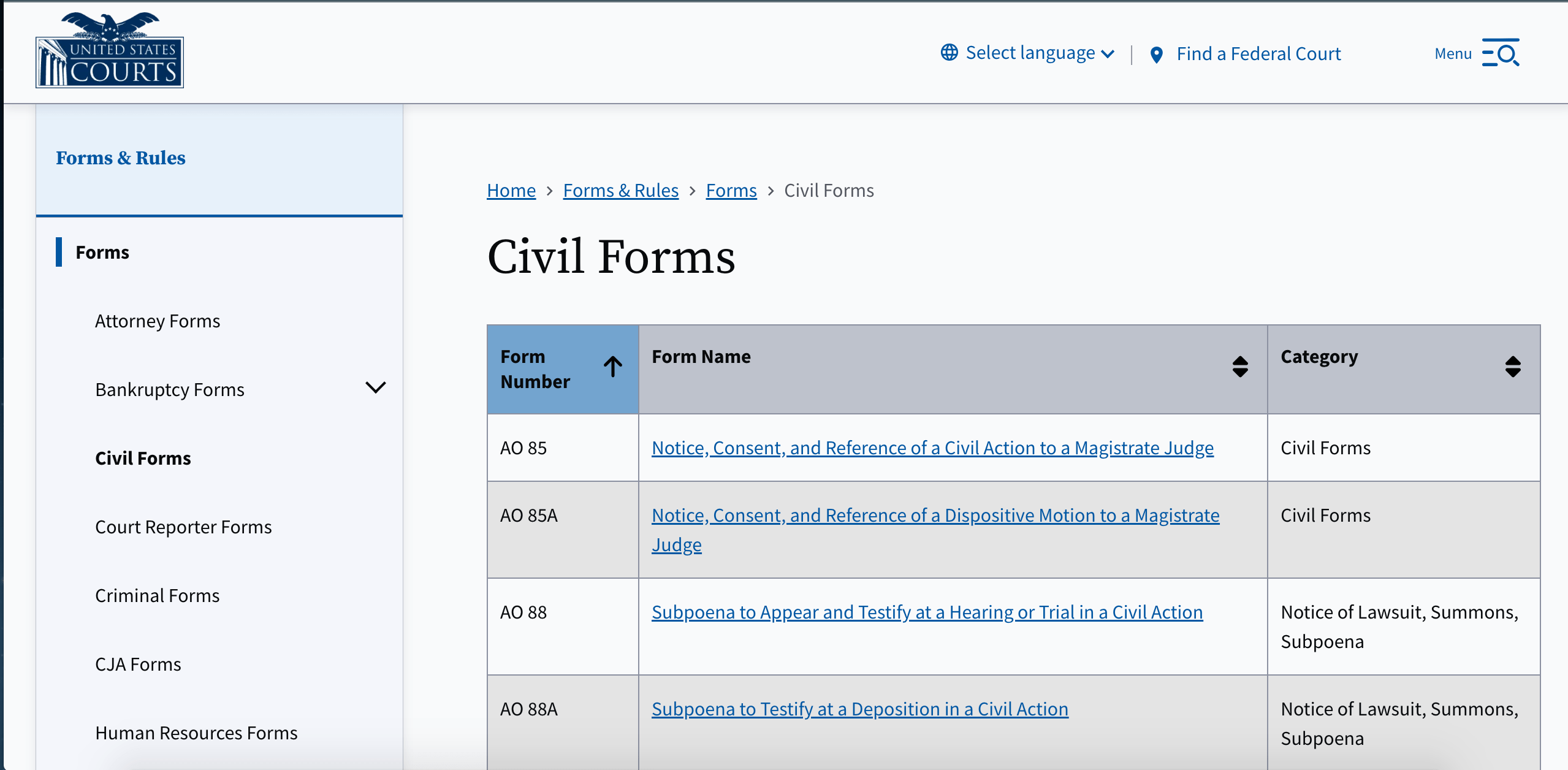
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Economic growth | National industries can fight |
| Lower tariffs | Risk of loss of employment in local sectors |
| Greater access to the market | Foreign trade dependence |
| Innovation and competition | Possible environmental concerns |
Public perception and impact of FTAs
- Inverter’s feeling: Financial markets generally react favorably to FTAs due to their growth and stability potential.
- Consumer point of view: Although FTAs allow more diverse products at lower prices, national employment security is a concern.
- Commercial point of view: Large companies have better access to the market, while small businesses find it difficult to compete with multinational corporations.
More complete free trade agreements in the world
- European Union (EU): Single market reduces commercial barriers between member states.
- FTA of the United States: Commercial agreements such as NAFTA (now USMCA) promoted by trade in North America.
- Indian Free Trade Agreement: India has implemented a series of FTA, including the India-Ea CEPA and India-objection, improving its commercial relations.
India-Australia Ecta: A modern TLC in action
One of the most notable examples of a modern and progressive free trade agreement is the Australia-India Economic Cooperation and Commercial Agreement (AI-ECTA)which entered into force in December 2022. This agreement reflects a new generation of FTAs that go beyond tariff cuts and address a broader economic integration, including services, investments and sectors focused on the future such as digital trade and sustainable development.
Key characteristics of Ai-Ecta
Ai-Ecta includes several prospective provisions that benefit Indian and Australian exporters:
- Tariff elimination: Australia eliminated tariffs on 100% of exports from Indian goods from the first day of the agreement.
- Reduced Indian duties: India has reduced tariffs on more than 85% of Australian exports, with a plan to extend this to 90% in 10 years.
- SUPPORT SUPPORT: The agreement promotes small and medium enterprises by improving transparency, cutting bureaucracy and encouraging bilateral collaborations.
- Simplified Customs: Faster and predictable customs authorization processes have been adopted to facilitate softer commercial flows.
- SERVICES AND PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION: Improved access for Australian education suppliers and better qualifications recognition support the mobility of the cross -border workforce.
SECTORIAL PROFITS AND COMMERCIAL IMPULSE
The ECTA has opened new opportunities in all sectors:
- For India: Free tax access for textiles, pharmaceutical products, jewels and engineering products in the Australian market has provided a significant competitive advantage.
- For Australia: Indian tariff cuts have increased wool exports, wine, legumes and premium agricultural products. In addition, Australian educational institutions have obtained a broader recognition and market scope in India.
Strategic and geopolitical meaning
Ai-Ecta is not just about economics, but is strategic:
- Trade diversification: Both nations aim to reduce the excessive dependence of traditional markets and promote the most resistant supply chains.
- Indo-Pacific Cooperation: The agreement strengthens the geopolitical alignment of India and Australia in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Way to the mint: Ai-Corte is an interim step towards a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA)that will further deepen bilateral trade.
Implications for future FTA
The success of Ai-Ecta demonstrates how modern NAFTAs are evolving to meet the demands of the 21st century economy. Its structure offers a plan for future agreements with key components such as:
- Digital commercial provisions
- Sustainability and green practices
- Improved labor mobility
- Mutual recognition of skills and qualifications
These elements are well aligned with the growing global emphasis on inclusive, fair and conscious environmentally environmentally.
Free trade zones: a Chinese case study
Chinese free areas have been established with the intention of attracting foreign investments and the advancement of exports. Some of the most consistent examples are:
- Shanghai Free Trade Zone (FTZ): China’s first FTZ, with an approach to releasing investments.
- Guangdong FTZ: Nourish high -tech companies and international commercial relations abroad.
Free trade areas versus free trade agreements
A free trade area differs from a FTA since it allows free trade of rates between member states without enforcing a common external rate for non -members. Examples include:
- Asia Pacific Agreement (APTA): Free trade area between India, China and other regional economies.
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC): Economic Union that encourages economic cooperation between countries in the Middle East.
Arguments against free trade and protectionism
- NATIONAL INDUSTRY PROTECTION: The government applies stronger protectionist policies to protect national companies to be saved.
- Challenge for developing countries: In a free economy, developing countries can be behind in terms of competitiveness.
- Labor and environmental concerns: With the increase in industrialization comes pollution and exhaustion of resources.
- National Security Risks: During geopolitical crises, trusting imports could represent a safety risk.
Future of the Global Free Trade Agreement
- New and emerging trade agreements: Nations continue to negotiate NAFT to facilitate stability and international economic trade.
- The emergence of digital trade: Internet trade and digital services are increasingly integrated in the newest FT ones.
- International commercial projections: Experts forecast the increase in regional commercial blocks and digital trade agreements.
- Green commercial practices: Future free trade agreements could contain mandatory clauses of ethical and environmentally sustainable commercial practices.
Conclusion: The role of NAFTA in global trade
Free trade agreements are vital to increase economic integration, reduce commercial barriers and create global interdependence. However, FTAs may have associated difficulties such as the interruption of the labor market, the dependence of associated nations and ethical trade practices. While world trade continues to evolve, digitalization and sustainability will prominently present in commercial pacts. The FTAs, with appropriate policies and laws, will continue to promote global development and economic growth.
How can Apho help
In afo, we specialize in:
- Help companies begin their export-import operations, including IES registration and political orientation
- DGFT and Customs Consulting Services: from early authorizations to EPCG, Canon, ROSCTLAnd more
- Extreme to end loading services, including customs authorization, transportation and container reserves
Asocate with us to navigate global trade with confidence, agility and strategic forecast.
#Understanding #free #trade #agreements #FTA #global #economic #impact