Fountain: AGU Advances
This is an authorized translation of an Eos article. 本文是Eos文章的授权翻译.
近年来,科学家们发现,基于机器学习的天气模型可以比传统模型更快地做出天气预测,且并且到第60天时就会开始模拟出不切实际的天气.
深度学习地球系统模型(Deep Learning Earth System Model,简称DLESyM)建立在两个并行运行的神经网络上:一个模拟海洋,另一个模拟大气。在模式运行期间,对海洋状况的预测每四个模式日更新一次。由于大气条件演变得更快,对大气的预测每12个模式小时更新一次。
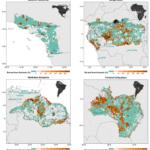
该模型的创建者Cresswell-Clay 等人发现,DLESyM与过去观测到的气候非常吻合,并能做出准确的短期预测。以地球当前的气候为基准,它还可以在不到12小时的计算时间内,准确模拟1000式比对计划第六阶段(CMIP6)的模型相当,甚至优于后者,CMIP6目前在计算气候研究中被广泛使用.
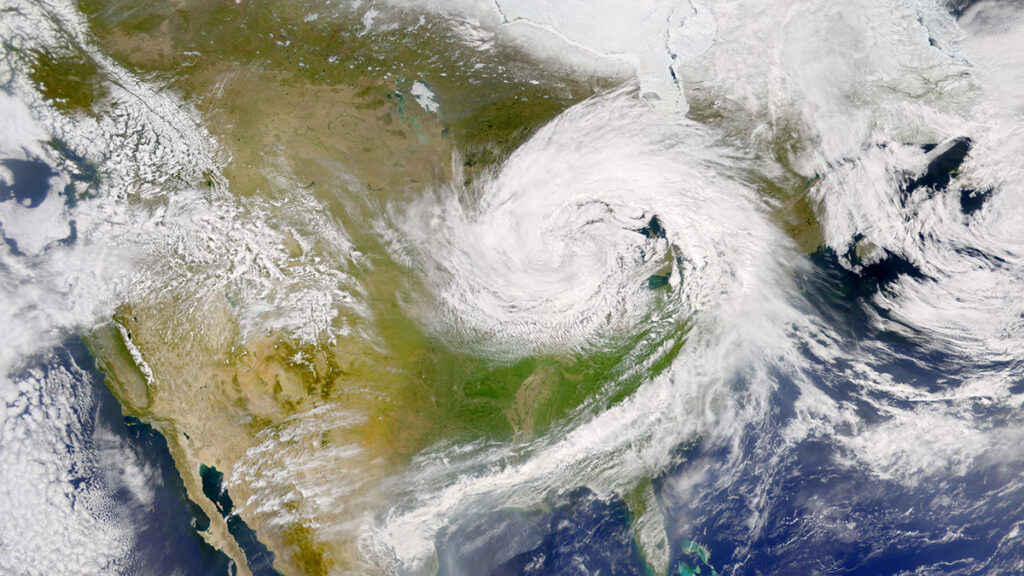
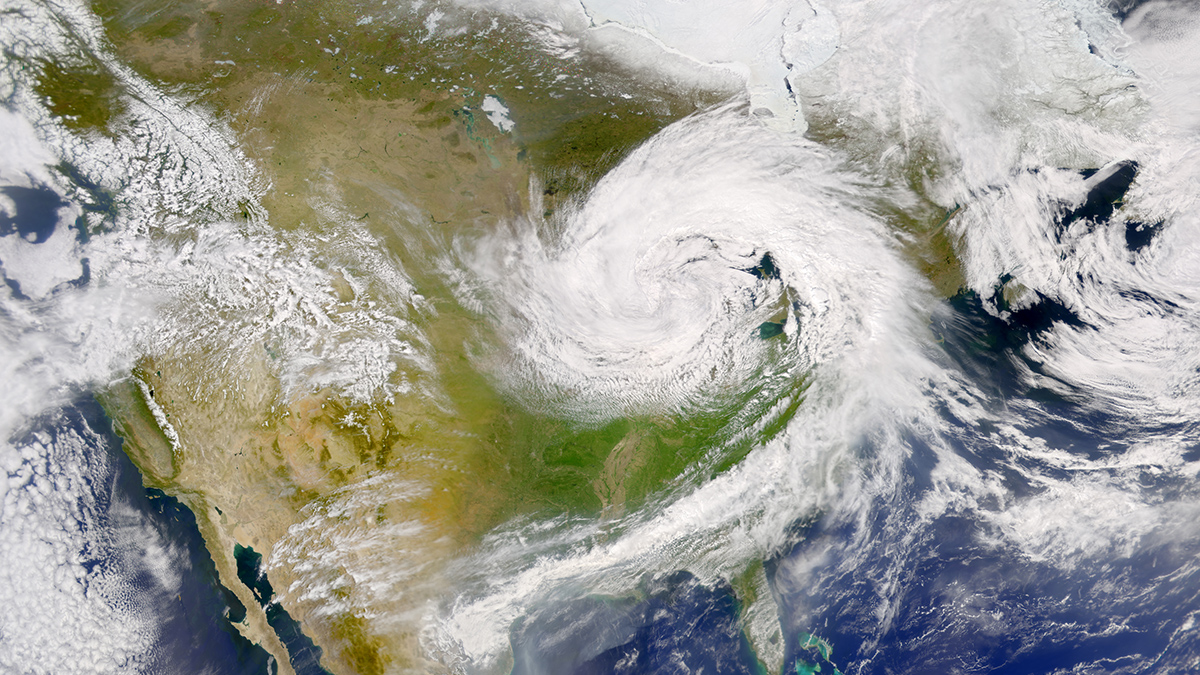
DLESyM 模型在模拟热带气旋和印度夏季季风方面优于 CMIP6 模型。它至少与CMIP6 1000年模拟结束时(3016 年)生成的东北风暴的结构与 2018 年观测到的东北风暴非常相似.
然而,新模型和CMIP6此外,对于中期预报(即未来 15天左右的预报),DLESyM DLESyM
DLESyM compliant, CMIP6 compliant (AGU Advances, https://doi.org/10.1029/2025AV0017062025)
—科学撰稿人Madeline Reinsel
This translation was done by wiley. 本文翻译由wiley提供。
Read this article on WeChat. 在微信上阅读本文.

Text © 2025. AGU. CC BY-NC-ND 3.0
Unless otherwise noted, images are subject to copyright. Any reuse is prohibited without the express permission of the copyright owner.
#机器学习模拟千年气候