Abstract
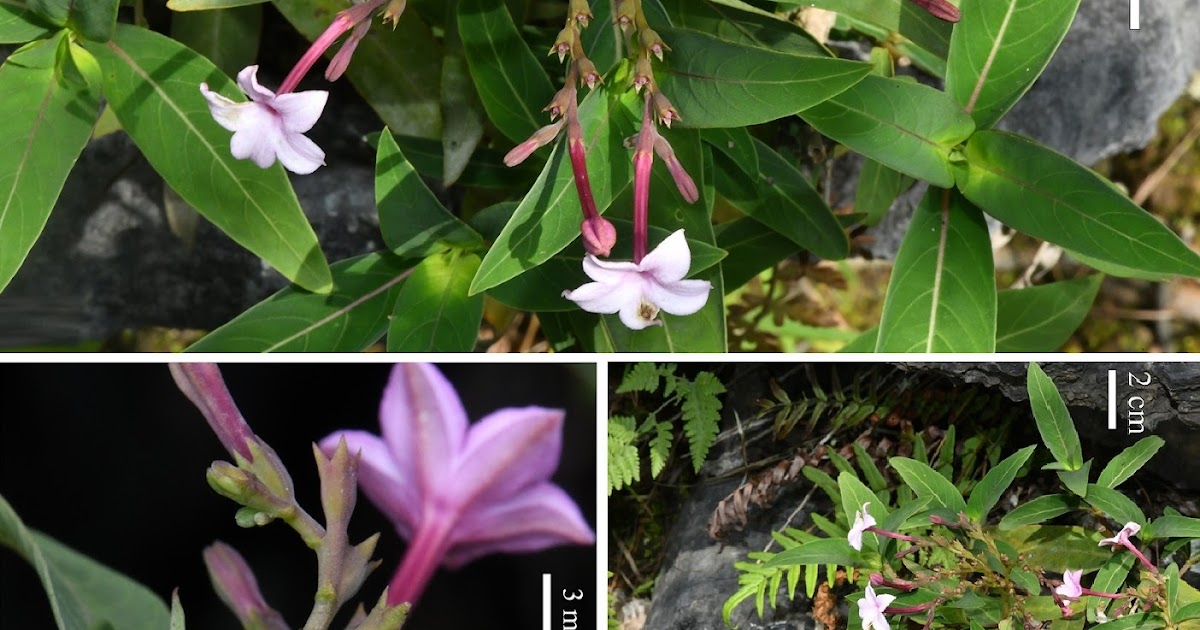
Escorpiura expiration (Rubiaceae), A new calcareous species It is located in Guangxi, China, describes and illustrates. This new species is similar to S. Coccinea, S. Scabrida, and S. Purpureocaerulea Having pubescent stems and subglobous capsules, but easily distinguished by its zincinous inflorescence and its triangular pubescent bracteols, 1 to 2 mm long. According to the IUCN criteria, it is considered poor in data (DD) until there is more information available. Photographs, an illustration, a distribution map and a comparative table with the most similar species are provided.
Keywords: Daxin County, limestone, new species, sink, taxonomy
Escorpiura expiration Y.nong and L.wu, sp. nov.
Chinese name: Xiē Wěi Luó xù cǎo (蝎尾螺序草).
Diagnosis: Escorpiura expiration It is more similar to S. coccinea, but it is different in its densely pubescent young stems that become glabrous when old , pubescent (1 to long vs. subulate, 3–4 mm long, glabrous), its puberulent calyx outside (vs. glabrescent outside) and its capsule of 3 to 4 mm in diameter. (vs. 4.5–5.5 mm in diameter).
Etymology. The specific epithet “Scorpiura“It refers to the terminal and cinchant inflorescences of the new species.
#Botany #Spiadiclis #Scorpiura #Rubiaceae #species #Guangxi #China