POT Lucy spacecraft He made a successful steering wheel of the second asteroid in his list of forced visits during the weekend, and sent images that document the strange form of double lobe of the elongated object.
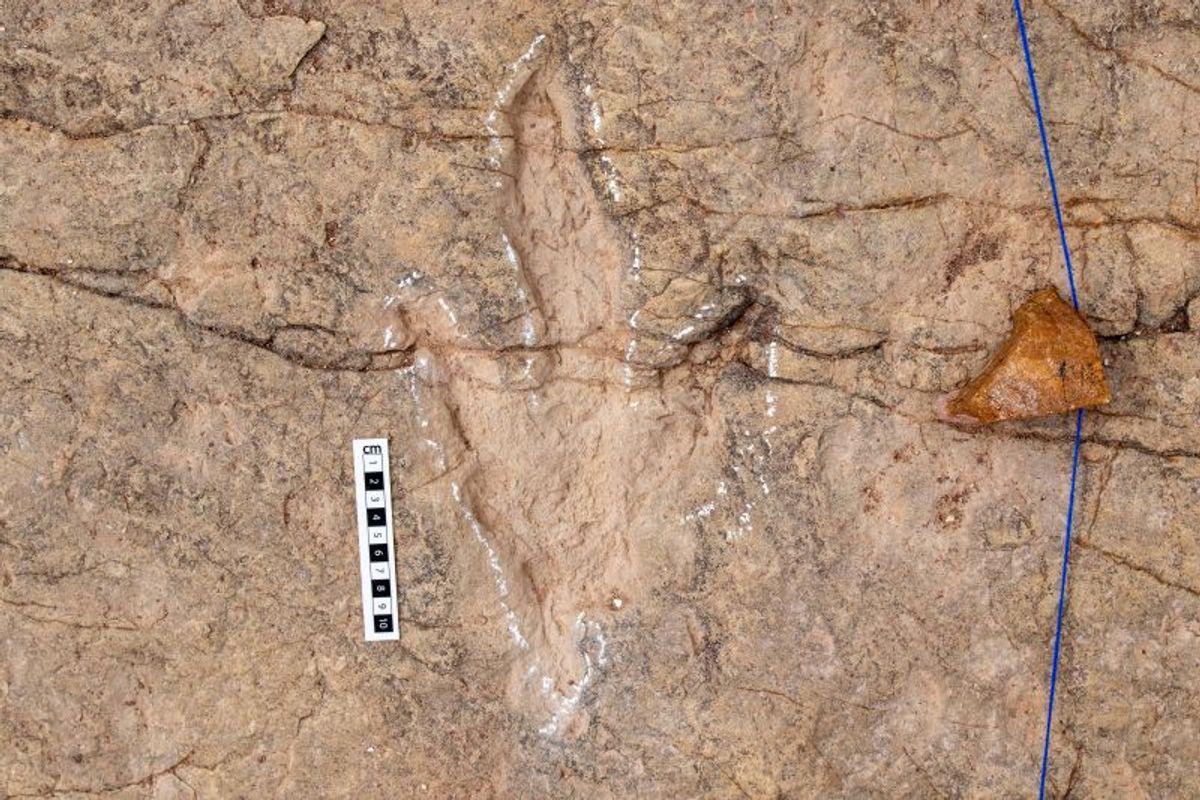
It turns out that the asteroid DonaldjoHanson – What is named after The anthropologist who discovered the fossils of a human ancestor called Lucy – It is what is known as a contact binary, with a couple of ridges in its narrow neck. In today warningNASA compares the limited structure with a couple of nested ice cream cones.
“Asteroid DonaldjoHanson has a surprisingly complicated geology,” said Hal Levison, a planetary scientist at the Southwest Research Institute who serves as the main researcher of the Lucy mission.
“As we study the complex structures in detail, they will reveal important information about the construction blocks and the collision processes that the planets formed in our solar system.”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mnblyvsy-pa FRAMBORDER = “0 ″ PERTER =” accelerometer; Autoplay; clipboard-writing; Encrypted half; gyroscope; image image; Web-Share “Referrerpolicy =” Strict-Origin-When-Cross-Origin “Permisscreen>
Lucy approached 600 miles (960 kilometers) to DonaldjoHanson on April 20, taking images every two seconds or so while passing. The images confirmed the state of the asteroid as a contact binary, that is, a compound object formed by the sticky collision of two smaller celestial bodies.
DonaldjoHanson is somewhat larger than was previously thought, with a length of approximately 5 miles (8 kilometers) and a width of 2 miles (3.5 kilometers) at the widest point.
The Easter meeting took place three and a half years later Lucy was releasedand 17 months after the 52 -feet -wide probe flew beyond its first target asteroid, Dinkineshand a mini moon called Selam. Like DonaldjoHanson, it was discovered that Selam was a contact binary.
The researchers consider that Lucy’s two meetings in the main asteroid belt, which is between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, are mere warming for the main event of the mission: a detailed study of the calls. Jupiter Troyano asteroids.
Such aleosids are harmlessly trapped at the resonance points in Jupiter’s orbit due to the gravitational influence of the giant planet. No spacecraft has approached a Jupiter Trojan.
Tom Statler, scientist of the NASA program for Lucy mission of $ 989 millionHe said that the quality of the first images demonstrates the “tremendous capabilities” of Lucy’s instruments.
“The potential to really open a new window to the history of our solar system when Lucy reaches Trojan asteroids is immense,” he said.
During the next few weeks, the researchers will recover, process and analyze the data of Lucy’s black and white images, as well as their images of images, infrared spectrometer and thermal infrared spectrometer. The spacecraft is scheduled to spend most of this year traveling through the main asteroid belt.
Lucy’s first meeting with a Jupiter Trojan asteroid, known as EurybatesIt must take place in August 2027. Four additional Trojan meetings will continue between 2027 and 2033.
This article was originally published by Universe today. Read the Original article.
#NASA #reveals #close #strange #asteroids #Sciencealert