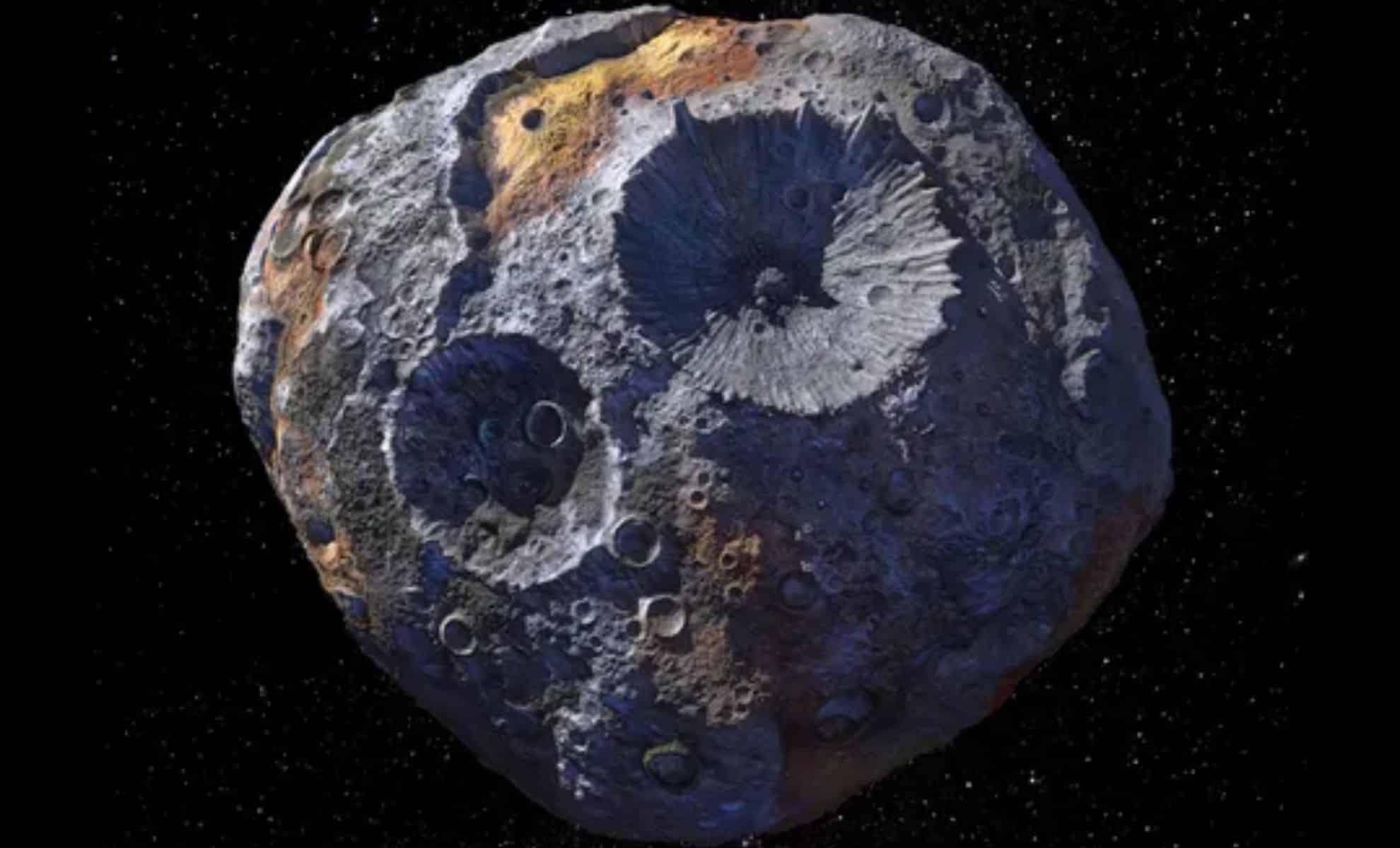
A recent study that uses data from the James Webb space telescope (JWST) has presented new ideas about the mysterious asteroid 16 psyche. Once it is believed to be a metallic remnant of the nucleus of a planet, psyche shows signs of hydration, which suggests a more complex story than was previously believed. These findings can offer important clues about the training of asteroid and the evolution of objects in the early solar system. Research, Available in ArxivIt shows that the psyche surface contains hydroxyl groups, which are generally associated with oxide formation. This discovery has led to a rethinking of the asteroid composition, which now seems to be a mixture of metal and silicate materials, possibly formed by the impacts of the asteroids rich in water. As scientists explore more, new ideas about the origins and nature of this heavenly body are emerging, challenging previous assumptions.
Hydration firm analysis
In March 2023, the infrared instruments of the James Webb space telescope, the near infrared spectrograph (Nirspec) and the Middle Infrared Instrument (Miri), directed their approach to the north pole of psyche. The resulting data revealed a hydroxyl firm on the surface of the asteroid, which suggests the presence of water in the form of oxide. Nirspec observations confirmed the presence of hydroxyl groups, which are commonly associated with water or hydrated minerals. Stephanie Jarmak, a planetary scientist at the Astrophysics Center of Harvard and Smithsonian, said that the detection of hydroxyl firms using JWST instruments “has helped other astronomers detect generalized molecular water on the moon, but it had not yet been used for wands.” This advance marks a significant advance in asteroid research and provides a clearer understanding of the materials that make up the psyche.
While Nirspec data confirmed the presence of hydroxyl groups, Miri’s data, which focuses on longer infrared wavelengths, did not detect a definitive water firm. However, Jarmak is still cautious, suggesting that water can still be present in psyche, although at too low levels for Miri to detect. Future observations, especially from the South Pole of the asteroid, could produce more definitive evidence, offering a clearer image of how hydrated materials are distributed through its surface.


Understand the mysterious origins of psyche
Psyche is a truly unique asteroid inside the main asteroid belt. Metering 173 miles (280 kilometers) at its broadest point, it is considerably larger than many other asteroids, and it is believed that its surface is rich in metal. Initially, scientists raised the hypothesis that psyche could be the exposed metal core of a planet that had suffered catastrophic collisions in the early solar system. However, over the years, the new data has challenged this hypothesis, which suggests that the asteroid can have a more complex composition.
The recent JWST findings add weight to the theory that psyche is not composed solely of metal. Instead, it seems to be a mixed world, with silicate and metal components. The presence of hydroxyl groups, indicating hydration, suggests that the psyche surface may have suffered similar processes to those of the earth and other planetary bodies. This raises the possibility that the psyche material was altered by impacts with hydrated asteroid impactors, which would have introduced water or water minerals on its surface. These new ideas could help researchers understand the formation and evolution of such objects, as well as their role in the development of the early solar system.
The future of psyche exploration
The discovery of hydroxyl groups and the possible oxide in the psyche is only the beginning of a deeper exploration in the origins of the asteroid. The ongoing psyche mission of NASA, which was launched in 2023, will reach the asteroid in 2029. Scientists are already planning additional studies to identify exactly where hydrated metals are found on the psyche surface. According to Jarmak, “future plans include studying exactly where metals are hydrated on the psyche surface.” One of the areas of interest is the southern pole of psyche, which contains a large crater that may have been created by an encounter with a hydrated impactor. This region will be critical to understand how the surface of the asteroid was molded by the impacts and the role that hydrated materials have played in their evolution.
The proximity of psyche and its unique composition make it a valuable objective for greater exploration. While mining efforts in psyche are not currently profitable due to their location at three times the distance of the Earth from the Sun, understanding its composition can provide crucial information for future space mining missions. If the surface rich in psyche metals contains water with water, could pave the way for mining companies in the future, although such efforts would need to address significant logistics challenges.
#expensive #asteroid #world #quadillion #oxidized #James #Webb #reveals #shocking #finding