- The kidney is the most important excretory organ of the frog.
- The frog excretes urea, ammonia and water.
- In the reborn, the kidney is a delivery, but in the adult kidney it is mesonéfic.
- The reborn is ammonotelic, while the adult is urreotelic.
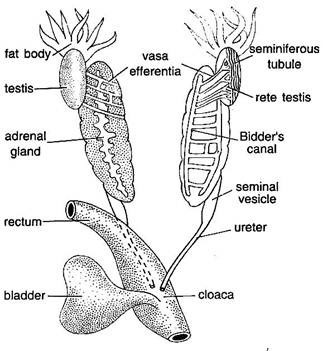
- The kidney is an related organ. It is found in the abdominal cavity within the sub-vertebral lymph.
- They are dark reddish. The dorsal and ventral surfaces are flat.
- A long supranal gland of light yellow is found on its dorsal surface. It works as an endocrine gland.
- The gonads are located towards the anterior end of the adrenal gland. Numerous thin structures in the form of finger surround these structures. These are the frog stored foods in fat bodies.
- From the outer ends of each kidney, a small channel emerges, which is known as the ureter.
- In the male frog, Ureter is called the Urino genital duct, because the sperm are also passed through this duct.
- These ducts are wider on the back of the kidneys known as seminal gallbladder.
- Urine is stored in this bag before fainting.
- The reborn is amonotelian.
Kidney functions:
- Regulates water in the body.
- Waste products are separated from the blood.
- The useful substances required for the body are reabsorb.
- Help in urine formation.
- Regulates the acidic and basic medium in the body.
- It produces blood corpuscles during the embryonic stage.
Internal structure of a kidney:
- Each kidney consists of numerous uriniferous tubules.
- The mesonophical kidney does not differ in cortex and marrow.
- The anterior end of each tubule ends in a structure similar to the cup called Bowman capsule. A lock of capillaries of blood is present.
- Both structures together form a Malfigian tubule.
- The malfigious tubules are shaped like ‘U’ and finally open in a transverse collection duct.
- Numerous collection ducts that merge to form a longitudinal collection duct or bastor channel and are linked with the ureter are present.
- Uriniferous tubules are hollow structures and the wall of your body is formed by glandular epithelium.
- The capsule and regions of the Bowman neck are ciliated and the rest of the posterior parts are not placed.
- There are four or five renal arteries, a renal holder vein and a dorso-lumbar vein that helps supply the kidneys.
- The blood is collected by four or five renal veins.
- Each artery is distributed in numerous small branches within the kidneys known as the afferent container.
- These branches are linked to the Bowman capsule and finally form a glomerulus.
- These numerous branches then bind or group together to form the efferent container.
- The efferent container passes through the Bowman capsule and goes down and makes a stuck network structure around the uriniferous tubules. This network forms a vénula and finally opens to the renal vein.

Frog excretory system
Excretion and its mechanism:
- The frog excretes urine in the form of urea. Such types of animals are called urootelic animals.
- Food particle proteins become amino acids after digestion. These amino acids decompose even more in pyruvic and ammonia acid after oxidation processes.
- The ammonia is very harmful to the body and internal organs. It is combined with blood carbon dioxide and becomes unstable urea.
- Urea is less toxic and less harmful than ammonia. It is soluble in water and becomes urine. The previous urine formation process can be divided into three parts:
- Ultrafiltration:
- The glomerulus is always in contact with the Bowman capsule and works as a filter.
- Blood passes very slowly through the glomerulus branches because its branches are very thin.
- 20% of water, urea, glucose and other substances are stored in the capsule capsule of Bowman and pass to the neck region.
- The ciliated epithelium helps or helps in this process and forms a soft substance known as ultra filtering.
- Reabsorption:
- Most substances are absorbed during the ultrafiltration process. In this step, only important substances are absorbed. Therefore, it is also known as selective absorption.
- Glucose, salts and water from the nearby parts of the tubules reabsorb of it.
- This reabsorbed filtering will be very difficult in condition.
- Excretion:
- The filtering is now transmitted to the lower end of U -shaped of the tubules.
- Here, the reabsorbed filtering is mixed with blood waste products. Blood waste products are absorbed by the uriniferous tubules network.
Excretory system in a frog
#Excretory #system #frog