- If the kidneys fail, toxic substances build up in the body until cells and organs begin to deteriorate and eventually die.
- Many tens of thousands of people around the world suffer from kidney failure, but a large number of them lead relatively normal lives thanks to the successful use of artificial kidney or hemodialysis therapy.
Working mechanism:
- The principle of diffusion is basic for the mechanism of operation of the artificial kidney.
- Simply put, the artificial kidney is a machine that pumps 5 to 6 liters of blood from the body through a hollow fiber dialyzer.
- The blood is flushed with a saline solution and sodium, potassium, and waste products such as urea, uric acid, excess water, and creatinine diffuse through the dialyzer using osmotic pressure.
- The cleaned blood is then returned to the body.
Procedure:
- One tube is permanently implanted in an artery (usually in the arm) and another is implanted in a nearby vein.
- During dialysis, tubes are connected to the machine.
- Blood is pumped from the artery through an oxygenated saline solution similar in ionic concentration to the body plasma.
- Because the waste concentration is higher than the normal concentration of the plasma-like fluid, the waste automatically diffuses through the semipermeable membrane of the tubes into this flushing fluid.
- The membrane is porous to all blood substances except proteins and red blood cells.
- Waste is removed from the body and purified blood can flow freely back to the body.
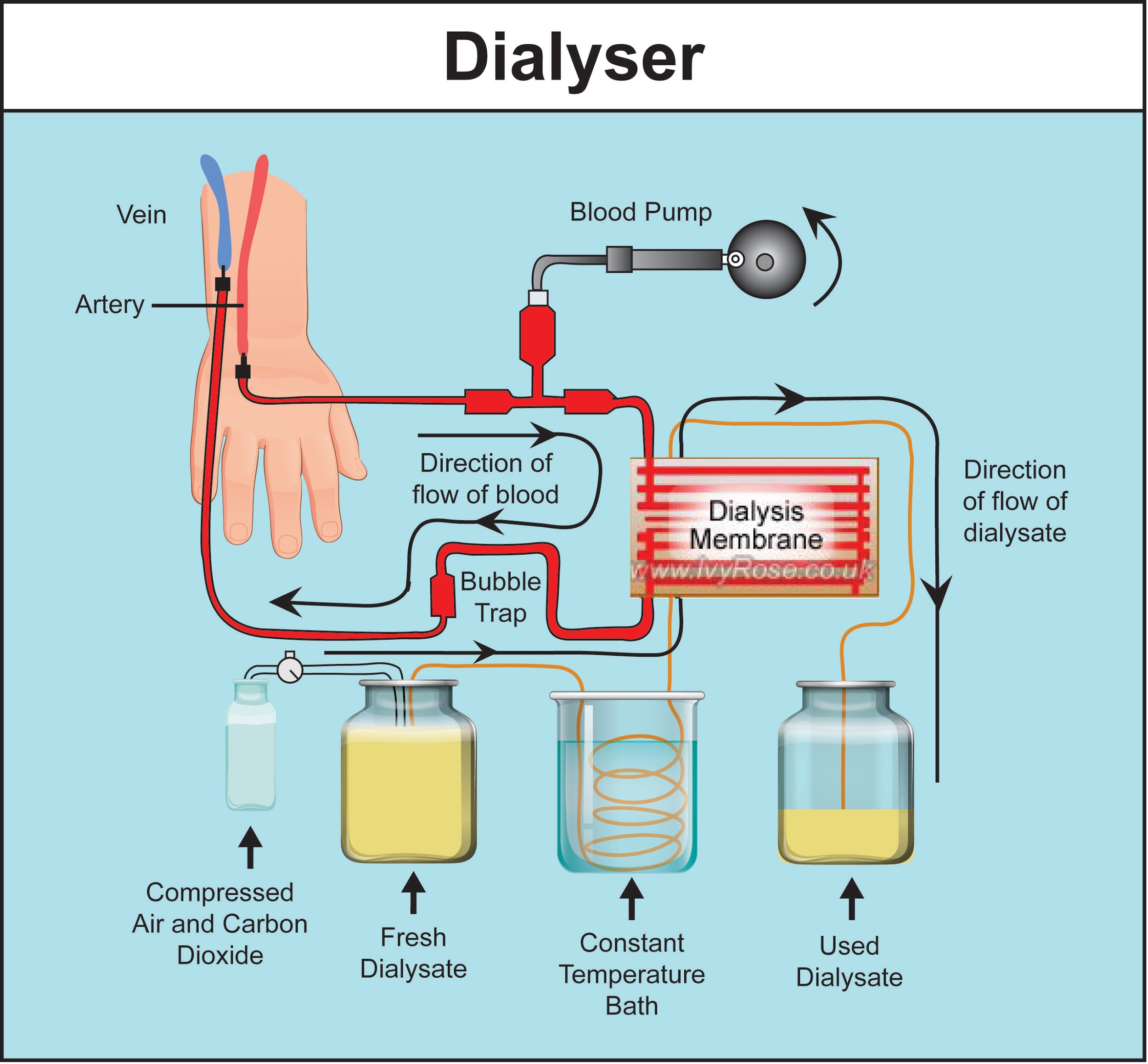
Source: https://nephcure.org/hemodialysis/
- Sometimes dialysis is also used to add nutrients to the blood. For example, large amounts of glucose can be added to saline so that the glucose can diffuse into the blood while waste is removed.
- It takes approximately 6 hours and 20 passes through bath fluid to complete a full dialysis cycle, and most patients receive treatment two or three times a week.
- Unfortunately, even this highly successful machine, which can remove waste from the blood 30 times faster than the natural kidney, provides only partial relief to kidney failure victims. All patients remain uremic (urine in the blood) to some extent.
Alternative method:
- Another method is peritoneal dialysis, which uses the patient’s peritoneal membrane instead of an artificial membrane for diffusion.
- The “clean” fluid (dialysis fluid) is injected into the peritoneal cavity every day for 3 to 4 days. Three daytime exchanges remain in the body for 5 hours each before being eliminated, and the fourth nighttime exchange remains in the body for 8 to 10 hours.
Artificial kidneys: hemodialysis therapy
#Artificial #Kidneys #Hemodialysis #Therapy #Scientific #Notes #Online