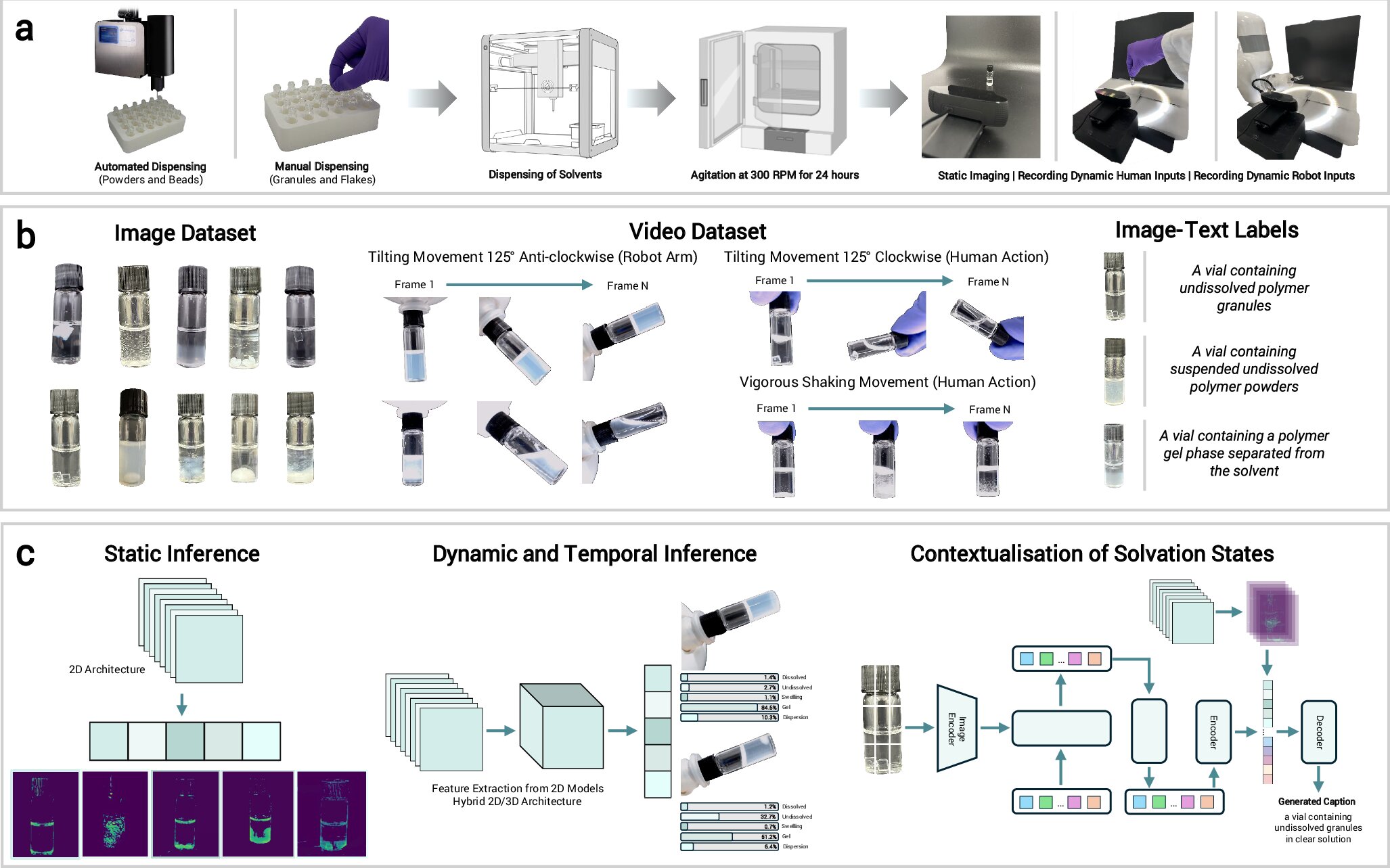
Experimental detection, generation of data sets and multimodular vision assistant. Credit: NPJ Computer Materials (2025). DOI: 10.1038/S41524-025-01658-7
A study published in NPJ Computer Materials It presents a new AI system that uses computer vision and language processing to interpret complex polymers -solvents interactions, such as swelling, gelation and dispersion of images and videos.
The document is entitled “A multimodel vision assistant for the autonomous interpretation of the solvation behaviors of polymers-solvents.”
Polymer systems -solver are remarkably difficult to analyze due to the variety of behaviors involved and the subjective nature of manual evaluations. This new approach integrates multiple AI models, including convolutional neural networks to understand static and dynamic visual data and a vision module -language that generates descriptive subtitles, providing an objective and scalable form of tracking and describing the phenomena of solveration.
“Polymers and solvents do not always behave predictably and human evaluations can vary,” said Liew. “Our AI assistant can see what is happening in detail and put it in words, which facilitates analyzing the data quickly and reliably, especially for high performance experiments.”
This system promises to accelerate the discovery of materials by allowing an automated and repeatable interpretation of the experimental results, eliminating bottlenecks caused by manual detection.
Work is part of Ph.D. Zheng Jie Liew research, supported by Ziad Elkhaiary, who contributed to the project while completing the Advanced Chemical Engineering Master (ACE) of the Department, under the supervision of Professor Alexei A. Lapkin in the Group of Engineering Research of Sustainable Reactions in the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology of the University of Cambridge.
The contribution of Elkhaienty during his mastery AS highlights the spirit of teaching led by the investigation of the department.
“It is gratifying to see our students actively mold the science of avant -garde,” Lapkin said. “Contributing to real projects prepares them for the challenges of sustainable chemical engineering.”
More information:
Zheng Jie Liew et al, Efficient multimodel vision assistant parameter for polymer solvation behavior inference, NPJ Computer Materials (2025). DOI: 10.1038/S41524-025-01658-7
Citation: AI System Decode Polymer-solvent Interactions for the discovery of materials (2025, July 10) Retrieved on July 15, 2025 from https://phys.org/news/2025-07-Ai-Decode-polyrsolvent-interacciones-materials.html
This document is subject to copyright. In addition to any fair treatment with the purpose of study or private research, you cannot reproduce any part without written permission. The content is provided only for information purposes.
#Polymer #interactions #School #decoding #system #discovery #materials