Techniques to deliberately alter the climate of the Earth, such as geoingeniery and planting clouds, have News After the devastating floods in Texas. While these approaches offer the potential for quick responses to certain climatic risks, they also come with significant uncertainties, ethical considerations and risks of unwanted environmental consequences. In the interview below, Kara D. Corderoan associated research scientist in the Earth and Environmental Engineering Department At the University of Columbia, it presents the underlying science of geo -enactment and the modification of the climate and analyzes its implications for future climate mitigation strategies.
What is geoyngeniery?
Climate geoyngenier refers to a series of large -scale techniques that are used to try to reduce the impacts of climate change. Some methods focus on the reduction of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, as through direct carbon capture or approaches that are directed to methane, a powerful greenhouse gas. Another set of methods, mentioned under the umbrella Solar Radiation Management (SRM), aims to increase the reflection of sunlight from the Earth’s atmosphere to cool the climate of the Earth. The most studied of these methods is the injection of stratospheric aerosol, which proposes to place sulfate aerosols at the top of the earth’s atmosphere to cool the climate (this is similar to the cooling effect that is observed after a large volcanic eruption, as Monte Pinatubo in 1991). Another method that is widely studied is Marine cloud shine. This technique is directed to the low clouds that are formed over the oceans and proposes to make these clouds more bright so that more sunlight is reflected to space. SRM methods have been studied mainly through modeling or laboratory, and They have not been displayed in the atmosphere at a significant scale.
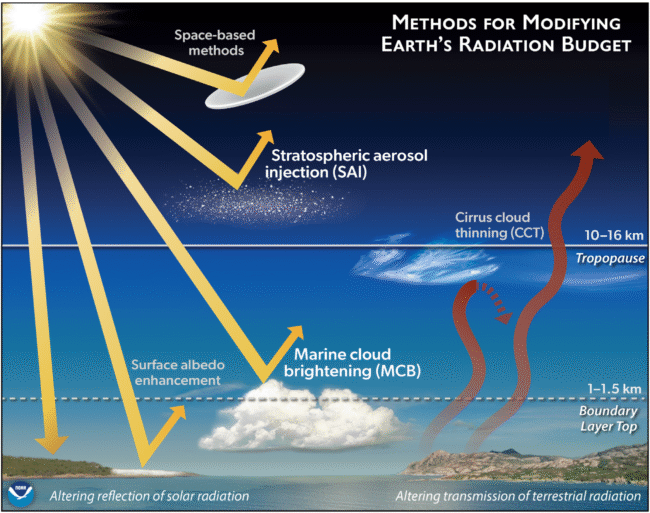
Estratosobric aerosol injection (SAI): A strategy to increase the number of small reflective aerosols in the stratosphere to increase the reflection of incoming sunlight.
Marine cloud shine (MCB): A strategy to add aerosol to the lower atmosphere on the oceanic regions to increase the reflectivity of low marine clouds.
Cloud thinning circle (CCT): A strategy to modify the properties of large altitude ice clouds to increase the transmission of outgoing land radiation to space.
Space -based methods: The proposed methods have considered mainly large “mirrors” in the space to reflect sunlight.
Surface Albedo improvement: Increased reflectivity of surfaces through, for example, white ceilings or changes in the ground lid.
What is the planting of clouds and how commonly practiced today?
Seed of clouds To increase precipitation and the snow layer has existed since the 1940s. This is generally known as “climate modification”, since the approach is in a short -term increase (on the scale of hours) in rain or snow. It is used in several Western United States where there are concerns about drought, as well as in many other countries in the world.
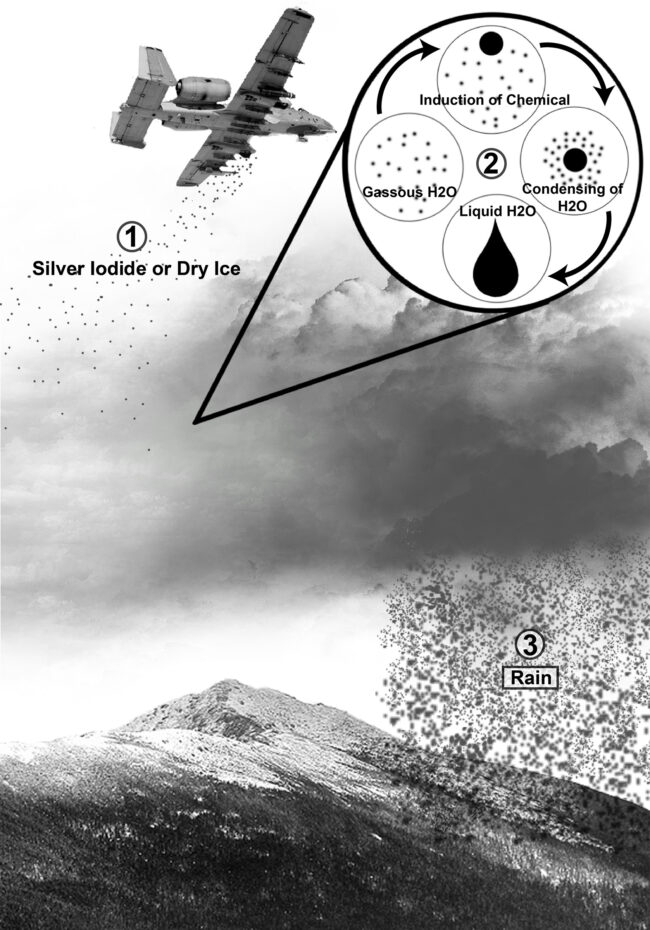
There are several different climate modification methods and approaches. Earl this year, my colleague Jared Donohue And I conducted a research study to create an accessible data set for recent climate modification in the United States by compiling records publicly available. Our article is still in review, but we discover that the most common approach in western United States has been to use silver iodide deployed by plane or land cannons in order to increase the snow layer. Silver iodide particles are dispersed in the cloud and, under certain conditions, can slightly increase the amount of precipitation (snow or rain) that results.
How effective is sowing in the clouds and could contribute to floods or other climatic extremes?
It is difficult to say exactly how well cloud planting works, because the climate naturally varies greatly, and the exact amounts of rain or snowfall in a given area are difficult to predict. But according to what we know about how clouds and rain are formed, cloud sowing does not cause a significant increase in precipitation. Most studies suggest that precipitation can increase by just 5-15%, compared to what would happen without cloud sowing.
What problems arise when we consider using geoyngenier to manipulate the climate of the earth?
We know that SRM will not simply cancel the effects of heating due to greenhouse gases (the atmosphere is much more complex than this), so it is not a replacement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. And there are ethical concerns because there is SRM potential to benefit some regions more than others. Our current models are not precise enough for us to understand and predict completely what these regional effects could be, so there is a need for better scientific understanding and a governance framework to face this type of challenges.
Is geo -ngealry a promising approach to address climate change?
Interest has been renewed in climate geo -ngealry as a potential way to reduce the immediate impacts of climate change, while long -term solutions for the reduction of greenhouse gases are sought. Although there is still much to learn, research in this area helps us better understand how the atmosphere works, which is important to understand both the weather and the weather. So, these areas definitely justify more research, but we are not yet in the stage in which we must consider using geo -scale on scale, and should not become a distraction of the need to reduce greenhouse gases.
#GEOINGENIERÍA #SEED #clouds #planet #status







