Abstract
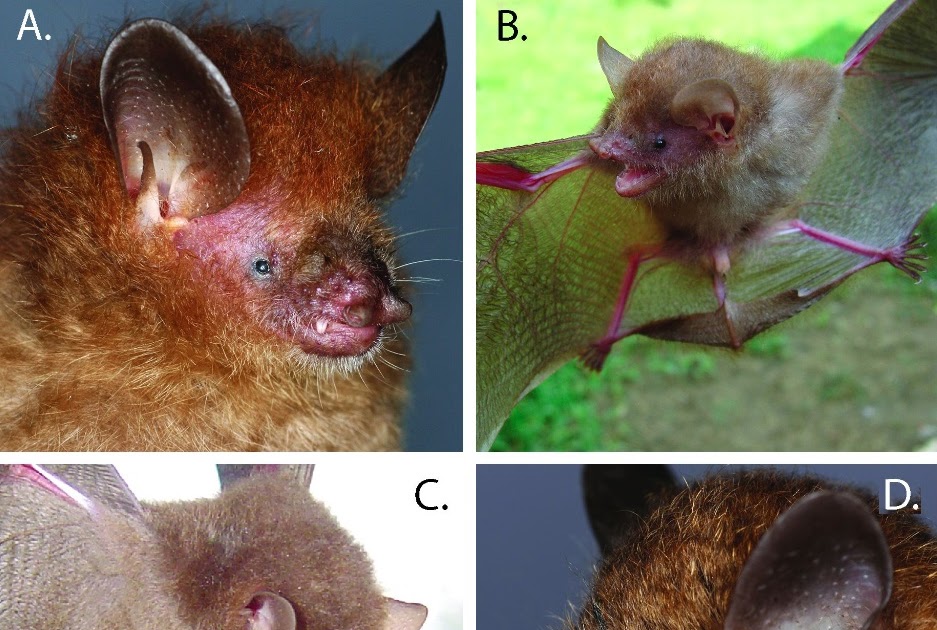
Murina It is a broad genre of insectivorous bats that occurs throughout Asia, whose known diversity has recently increased with the description of 26 new species in the last 20 years. The Filipino archipelago, mainly composed of islands with oceanic origin and, therefore, an isolation history, has produced a fauna rich in endemic species, including bats. Here, we describe morphological and genetic diversity between Murina The specimens collected from the Philippine Islands compare them with representatives of Southeast Continental Southeast and the adjacent islands. Our results show that the broad M. Cyclotis represents a radiation, starting around 11 mya, of five different Murina Endemic species of the Philippines, including three endemic of a single island. These five new ones M. Cyclotis Group species are mainly allopatric distribution, with the exception of two species, the smallest and largest that occur in the Philippines, which coexist on the Mindanao Island. Our study documents Murina Suilla, a species that occurs in Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand, and only occurs in the Mindoro and Palawan Islands within the Philippines. In addition, we describe a new species that is a sister for M. Suilla and is widespread in the Filipino archipelago. In general, our study has increased the number of Filipino Murina species of two to seven. As the first phylogeographic analysis of a genus of laryngeal ecolocation bat within the Philippines, our study provides evidence that the diversification of insectivorous bats of the sotobosque resonates to a large extent that the batélagos of the fruit (pteropodidae), which is characterized by the latest Philippi They condemn the latest regions of the modern islands of the modern islands of the last ages, which connect to the last ages, which connect to the last ages, which are condemned to the last ages, which are condemned to the last ages, which are connected the last ages, which are endemic, which are condemned to the last ages, which are related to the late age. Oceanic Islands. We presume that the subsequent phylogeographic investigations of other BAT taxa can reveal similar endemic radiation, previously not recognized, within the highly biodiverse philippines.
Mammalia, diversification, endemism, myocene, phylogeny, oceanic islands, species limits, Southeast Asia
#Evenings #Philippines #descriptions #species