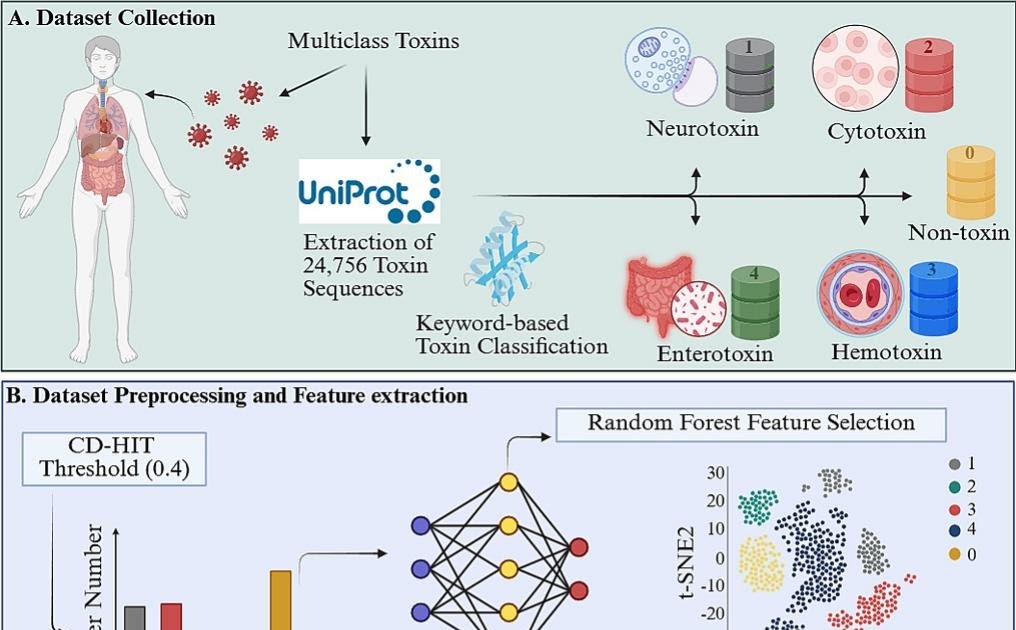
Understanding the structural and functional diversity of toxin proteins is critical to elucidate macromolecular behavior, mechanistic variability and structure bioactivity. Traditional approaches have mainly focused on binary toxicity prediction, offering a limited resolution to different modes of action of toxins. Here we present MultipleA set of stacking for the classification of toxin proteins based on its molecular mode of action: neurotoxins, cytotoxins, hemotoxins and enterotoxins. We commented a comprehensive data set of 24,756 proteins (20,361 toxins and 4395 no toxins) and we extracted High Dimension ESM-2 inlays that encode evolutionary, structural and biochemical characteristics. The two -level stacking frame integrates LGBM, MLP, ET, KNN and QDA as base classifiers and XGBOOST as a metacclassifier. Multitox achieved a general accuracy of 91.07 %, a 90.73 %F1 score and a Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) of 91,61 %. Class details were 93.75 % (neurotoxins), 87.79 % (cytotoxins), 98.80 % (hemotoxins), 97.02 % (enterotoxins) and 95.83 % (toxins versus non -toxins). The interpretation and correlation based on the form with known physicochemical descriptors revealed specific characteristics of the class linked to biologically significant patterns in structural motifs, hydrophobicity and accessibility of solvents. Functional annotations using interproscano, groups of orthologists and secretion signal analysis identified specific signatures of the toxin class related to folding, location and host interactions. We implement a public web server (https://cosylab.iitd.edu.in/multitox/) for real -time predictions and batch mode. Multitox provides a scalable and biologically interpretable frame for protein classification, union sequence data with functional ideas.
Sharma, H., Thakur, MS, Barala, A., Khan, MS, Bhagat, S. and Bagler, G. (2025). Multix: An a sequence -based stacked set for the classification of multiclase protein toxins. Biological Macromolecules International Magazine, 327147399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiomac.2025.147399
#sequence #based #stacked #set #model #multiclase #protein #toxins #classification