Fast facts
Where is? Grand Erg Oriental, Sahara [30.13306820, 9.306920931]
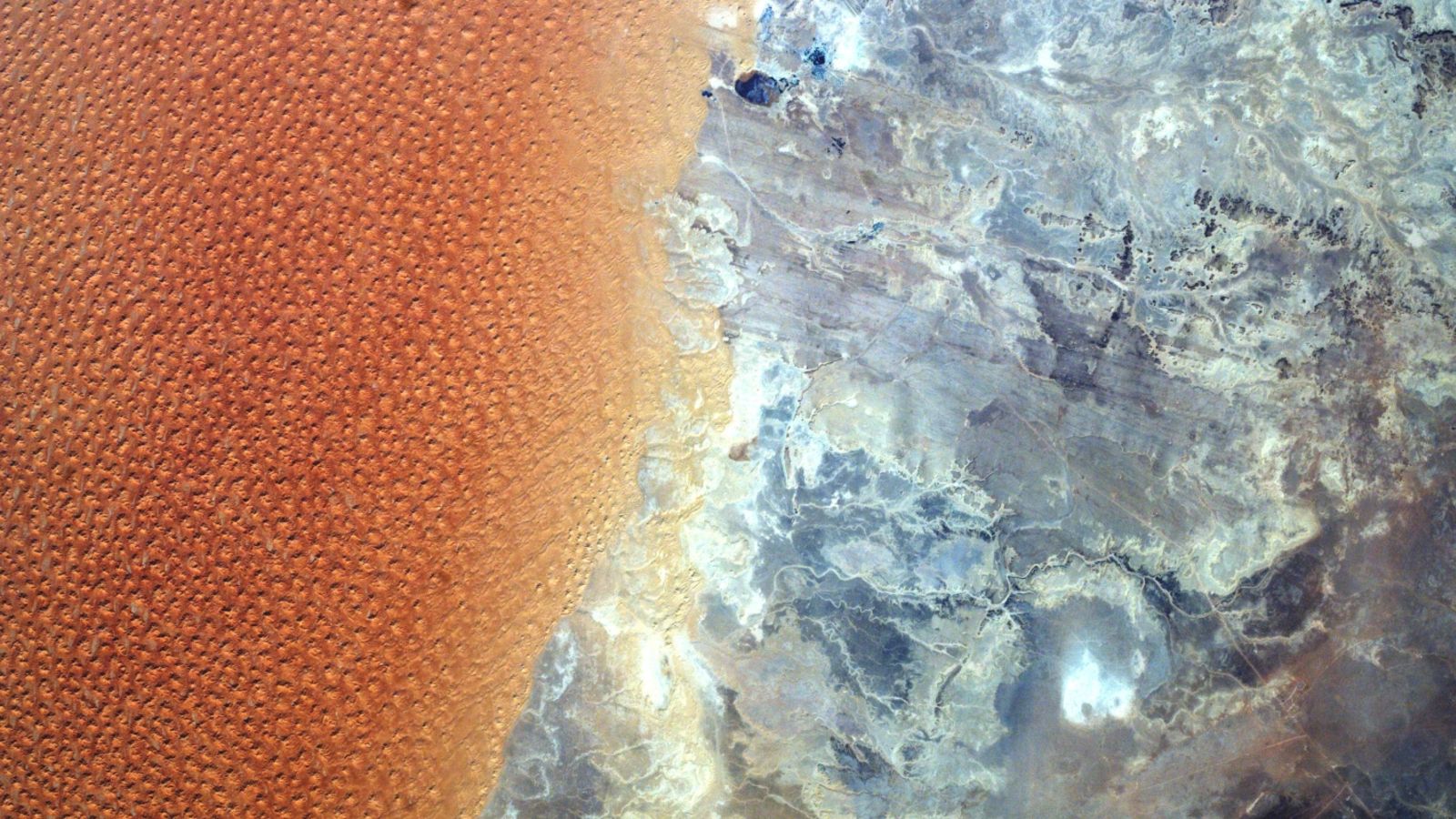
What is in the photo? The marking contrast where a “Star dunes” field meets Rocky Hills
What satellite took the photo? Camera Earthkam, aboard the International Space Station
When was it taken? October 31, 2017
This surprising satellite image shows the marked difference between a giant field of sandy “stars” and an arid rock desert in the Sahara desert. Contrasting biomes also overlap with the border where two African countries are located.
The visible orange sand in this image is part of the Eastern Grand Erg: a giant dune field, or ERG, which covers about 55,000 square miles (140,000 square kilometers) in the north of the Sahara.
This part of the ERG has hundreds of prominent “star dunes”, which have at least three ridges from a central peak, giving them a Appearance similar to the star when seen from above. Star dunes can grow to have more than 300 feet (90 meters) high and are only formed in places where wind instructions constantly change, allowing their different slopes to be formed, according to the National Parks Service.
The dunes overlap with a rocky wind whipped by the wind, which is among the “driest parts of the Sahara desert” and almost completely devoid of vegetation, according to NASA Earth Observatory. This land is covered with overlapping geological characteristics, which gives it a quality of another world.
One of the most striking characteristics is a great white patch in the heart of the rocky terrain, which is the remnant of an old lake. You can also see a series of parallel grooves in the rock (in the upper half of the rocky terrain), which were carved by unidirectional winds that blew long before multiple sides were formed.
Related: See all the best images on Earth from space

The dunes in the image are located within Algeria, while most of the rocky terrain is in Libya. The invisible limit between the two countries is largely in the center of this image. However, at one time, right to the left of a Libyan city called Ghadames (visible as a dark point near the top of the image), the border between the countries overlaps almost exactly with the line where sand and rock are located.
While contrasting ecosystems seem to have nothing to do with each other, they are more linked than you imagine. Geologists believe that the majority of the ERG sand was deposited by the old rainwater that took loose sediments of the rocky terrain and threw them into a natural depression or sinking in the landscape.
It is likely that this process will take hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of years, and if you look closely, you can see that part of the ERG sand has spilled in the old “sinuous water courses” that helped deposit the sand inside the ERG, according to the Earth Observatory.
The ERG is also partly formed on the bed of an old river. When the rain falls shortly on the ERG sands, moisture is channeled to underground aquifers, which can withstand vegetation pockets on the surface. If this did not happen, this valuable humidity would quickly evaporate to the atmosphere.
#Sea #clashes #star #dunas #sea #land #world #countries #land #space