Oxides containing RB of hut and stable expand the possibilities for sustainable oxide ion conductors. Credit: Tokyo Institute of Sciences
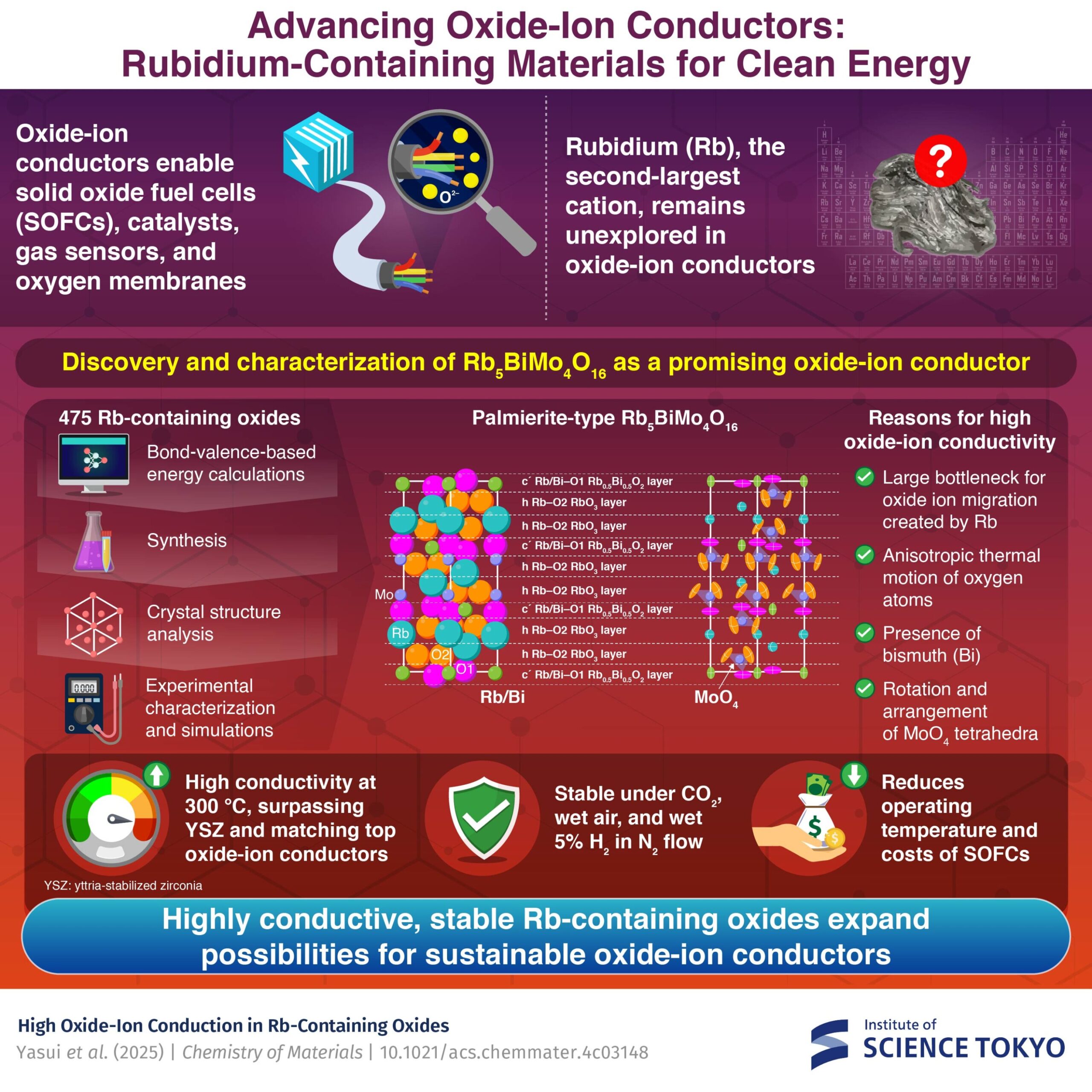
Rubidium could be the following key player in oxide ion conductors. Researchers from the Tokyo Institute of Sciences have discovered an oxide ion driver containing weird (RB), RB, RB5Bimo4EITHER16with exceptionally high conductivity.
Identified through computational detection and experiments, its higher performance comes from low activation energy and structural characteristics such as the large free volume and tetrahedral movement. Its stability in various conditions offers a promising direction for solid oxide fuel cells and clean energy technologies.
Oxide ion conductors allow oxide ions (or2-) to be transported in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC), which can work with various fuels beyond hydrogen, including natural gas and biogas, and even certain liquid hydrocarbons. This flexibility makes them particularly valuable during the transition to a hydrogen economy.
While SOFCs have a transformative potential from an energy sustainability perspective, their generalized adoption is still challenged for their cost, durability and operating temperature range.
Overcoming these obstacles requires the development of better oxide ion conductors, and researchers in the world are constantly testing new materials with different chemical compositions. Could Rubidio (RB) be the key to high -performance oxide ions?
The research team, led by Professor Masatomo Yashima in the Department of Chemistry, School of Sciences, set out to answer this question.
They explored RB unleashed potential as the next important advance in oxide ion conductors technology through a systematic and comprehensive approach. His findings were published online in Materials chemistry.
From RB+ + It is one of the largest cations (second only to the ion of Cesium), the crystalline oxides containing RB are expected to have a larger network and free volumes, which can lead to a lower activation energy for the conductivity of the oxide ions.
Based on this idea, the researchers first performed a computational detection of 475 oxides containing RB using energy -based energy calculations. They discovered that palmierite type oxide materials, which have a crystalline structure similar to natural mineral palmierite, exhibited a relatively low energy barrier for migration of oxide ions.
Taking into account that several materials containing bismuth (BI) and oxides contain5Bimo4EITHER16 as a promising candidate.
To validate their selection, they conducted a series of experiments, which include material synthesis, conductivity measurements, chemical and electrical stability tests and detailed composition and crystal structure analysis. They also performed theoretical calculations and simulations of molecular dynamics AB Initio to explore the underlying mechanisms behind the measured properties.
The results were very promising. As Yashima says, “surprisingly, RB5Bimo4EITHER16 He exhibited a high conductivity of oxide ions of 0.14 ms/cm at 300 ° C, which is 29 times greater than that of YTTRY CIRCONIZED at 300 ° C and comparable to the main oxide ion conductors with similar tetrahedral ions. “
The research team identified several factors to explain this exceptional conductivity of oxide ions. First, the great RB atoms facilitate low activation energy for the conductivity of oxide ions. This conductivity of the oxide ions is further improved by the rotation and disposition of the MOO4 tetrahedra inside the glass network.
In addition, large anisotropic thermal vibration of oxygen atoms in the material also contributes to the conductivity of oxide ions. Finally, the presence of large bi cations with a solitary electron pair also plays an important role in reducing activation energy for migration of oxide ions.
Another remarkable aspect of RB5Bimo4EITHER16 It is its stability at high temperatures in various conditions, including co2 Flow, wet air flow, 5% wet hydrogen in the flow of nitrogen and its stability at approximately 21 ° C in water.
“The discovery of oxides containing RB with high conductivity and high stability can open a new way for the development of oxide ion conductors,” adds Yashima.
“We hope that these advances lead to new applications and RB markets, in addition to contributing to reducing the operating temperature and reducing the cost of solid oxide fuel cells.”
Additional research in this field could pave the way for better oxide ion conductors in energy applications focused on sustainability, as well as devices such as oxygen membranes, gas sensors and catalysts.
More information:
Yuta Yasui et al, high conduction of oxide ions in oxides containing RB, Materials chemistry (2025). DOI: 10.1021/ACS.HEMMATER.4C03148
Citation: The material that contains rubidium with exceptional conductivity and stability could pave next-generation fuel cells (2025, February 21) recovered on February 27, 2025 from https://phys.org/news/2025-02-rubidium-material-exceptional-stability-pa
This document is subject to copyright. In addition to any fair treatment with the purpose of study or private research, you cannot reproduce any part without written permission. The content is provided only for information purposes.
#material #rubidium #exceptional #conductivity #stability #pave #path #generation #fuel #cells